Does GA4 Use Cookies? Cookies in Google Analytics 2024
Updated: 3/8/24 Cookies are an important part of generating the data for digital analytics. And the increasingly complex privacy environment means GA4 cookies are under the microscope, especially in the EU. But what are cookies exactly? And what role do they play in Google Analytics now?
You’ll learn that in this article, including how to immediately delete cookies in GA4.
Table of Contents
- What are cookies in web analytics
- Does GA4 use cookies
- Consent mode v2 and GA4 cookies
- How do cookies work in GA4
- Benefits of first party cookies
- How long do GA4 cookies last
- How to expire cookies in GA4
- Third party cookies
- GA4 will be less reliant on cookies?
What Are Cookies in Web Analytics?
Cookies are small files that store data about web users.
Cookies came onto the scene in 1994. Today, cookies provide tracking in web analytics and in digital marketing in general. There are two primary types of cookies: first party cookies and third party cookies.
What Are First Party Cookies?
First-party cookies are created and managed by the website domain the user is currently visiting.
You’re currently on the domain rootandbranchgroup.com (Hi, there!). A cookie is helping to track what you are up to. It doesn’t know who you are, but it does know if you’ve been here before or if you’re here for the first time. It knows because it checks to see if there is already a cookie in your browser from this website.
The tracking is limited to this site only. Once you leave, none of that information “does” anything other than being available in web analytics data so I can understand how people use the site so I can try to make it better.
What Are Third Party Cookies?
Third party cookies are not limited to a single domain. Instead, they track web visitors across multiple websites and create a comprehensive picture of user behavior.
As you can imagine, digital advertising platforms love third party cookies because they allow detailed ad targeting capabilities. Privacy advocates and many humans do not love third party cookies.
Does GA4 Use Cookies?
Yes. Google Analytics 4 uses first party cookies. First party cookies identify unique users and are identified with individual sessions (visits).
Google says that Google Analytics is designed to work with or without cookies. When cookies are not available for a given session, Google will fill in the gaps of data based on modeling.
For example, let’s say you can track 80% of your form submission conversions with cookies. Google Analytics knows where those sessions come from (because of the cookies) for the purposes of “attribution” (i.e. giving credit to the proper traffic sources for sending that converting traffic).
But what happens for the remaining 20% of sessions that were not tracked with cookies?
Google will compensate for the “missing” cookie data, by using all of its pre-existing data to model where it thinks those remaining 20% of conversions would have come from.
Why Might Cookies Not Be Available?
Here are two reasons:
- Your web visitor is using a browser like Brave that blocks cookies.
- You have a cookie acceptance banner on your site and your web visitors do not consent to cookies.
Cookie consent is an increasingly important topic in digital marketing in 2024. Legislation like the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and DMA (Digital Markets Act) is forcing Google to take a more privacy-centric approach, especially in the EEA (European Economic Area).
That’s one of the important factors behind Google’s consent mode v2, which deals directly with GA4 cookies.
Consent Mode V2 and Cookies in GA4
Consent mode is a mechanism by which your website communicates visitor privacy choices to Google. Those privacy choices are made on cookie banners like the one below. Google tags can then adjust how they fire and process data.
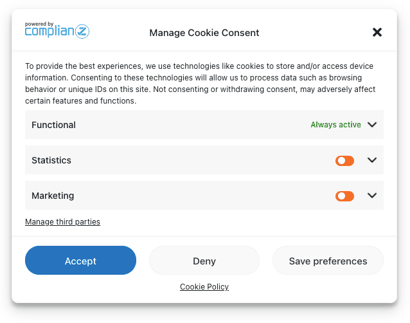
There are two operating modes for consent mode: “Basic” and “Advanced.”
What is Basic Consent Mode?
With Basic consent mode Google tags are prevented from running and collecting data until your visitor consents to data collection.
If you implement basic consent mode you will only be able to track visitors who grant consent to be tracked with Google Analytics. If a visitor denies cookies through the cookie banner or ignores the cookie banner, the visitor will not be tracked with cookies.
What is Advanced Consent Mode?
With Advanced consent mode Google tags will load before the consent banner appears on the page. If a visitor does not consent to cookies, the tags will still send “pings” (without cookies) to Google. These “cookieless pings” will help Google to provide modeled data for the GA4 property. Precisely how these pings work is not yet something that Google has described.
Leaving aside these “pings” for the time being, let’s look at how real cookies work in GA4.
So How Do Cookies Work in Google Analytics?
In the context of GA4, first-party cookies are set by the analytics.js library, allowing the collection of data directly from a website visitor.
Some of this data is about what visitors do on a website. This is all about tracking those GA4 events like clicks, scrolls, file downloads, page views, and more. Some of the data provides additional context about the visitors themselves. Where did they come from? Have they been on the site before?
What is analytics.js?
It’s a Javascript library that is used to measure interactions on your website. When we refer to what Google Analytics collects, we’re referring to this library.
Which Cookies Does GA4 Set?
Google Analytics 4 sets two different cookies by analytics.js.
The _ga cookie distinguishes users from one another. The _ga_<container-id> cookie is used for session state data. Each of them have a default expiration time of 2 years.
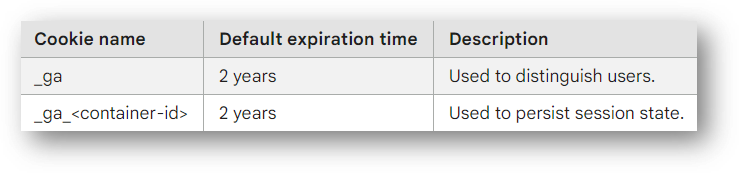
The table above is from the Google Analytics support article here.
Here’s how it works:
When a user visits a website, the analytics.js library creates a first-party cookie that stores information such as the user’s unique identifier, session details, and website interactions. This data is then sent to the Google Analytics servers, where it is processed and transformed into reports. That is the data that we can then see in our GA4 reports and Explorations.
Some Benefits of First Party Cookies
These are some of the benefits first party cookies can bring.
- Personalization: First-party cookies allow website owners to deliver personalized content and experiences to their visitors. By tracking user behavior and preferences, businesses can tailor their offerings and visitor experience.
- Cross-Domain Tracking: GA4 allows the tracking of users across multiple domains using first-party cookies. This functionality enables a more holistic view of user interactions across various web properties owned by the same organization.
- Better User Privacy: First-party cookies can be accessed by the domain that created them. This stands in contrast to third party cookies which are set by a website other than the one that is currently being visited.
First party cookies are generally considered the “good” cookies, even among data privacy advocates. They can make the internet a more useable place without the same level of privacy risk coming from third party cookies.
How Long Do GA4 Cookies Last?
The default behavior is for GA4 cookies to persist for 2 years of inactivity. However, you can customize this by overriding the default cookie settings.
Read on below to customize your cookie settings.
How to Expire Cookies in GA4
If you want, you can set cookies to expire immediately in GA4. If you do, you won’t be able to see things like new vs. returning visitors since all visitors will appear to be new.
But you can dramatically cut down on your GA4 cookies by setting them to expire immediately at the end of the session. That way, they can assist in tracking the individual session data but they will disappear after. If you want to try a code based approach, this article from Stack Overflow might be worth testing (note: I haven’t tried it).
Here’s how to expire your cookies immediately.
First, go to the “Admin” section of your GA4 property and click into “Data Streams”. You can find it one of two places as shown below.
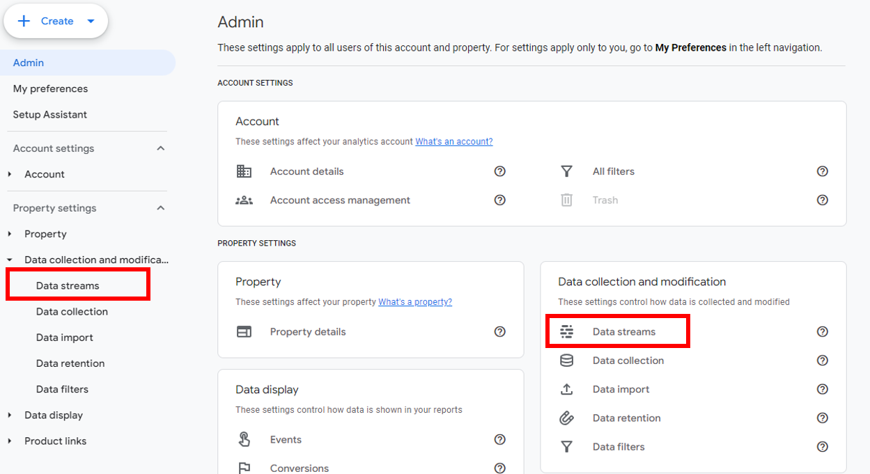
Now, select your individual Data Stream. If you’re only tracking a website and not an app, you should see a single web data stream to choose.
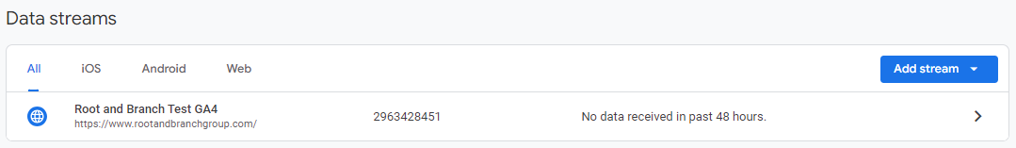
Next, scroll down and click ‘Configure tag settings’ under the Google tag area.
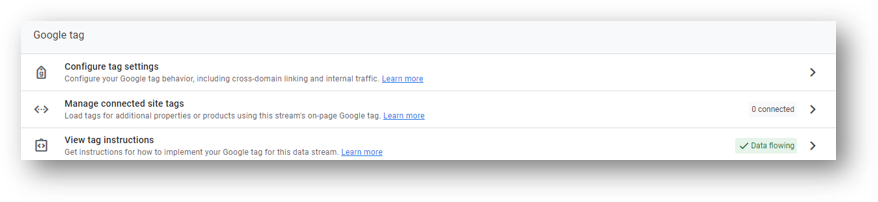
Once you’re viewing your tag settings, click the blue ‘Show all’ button.
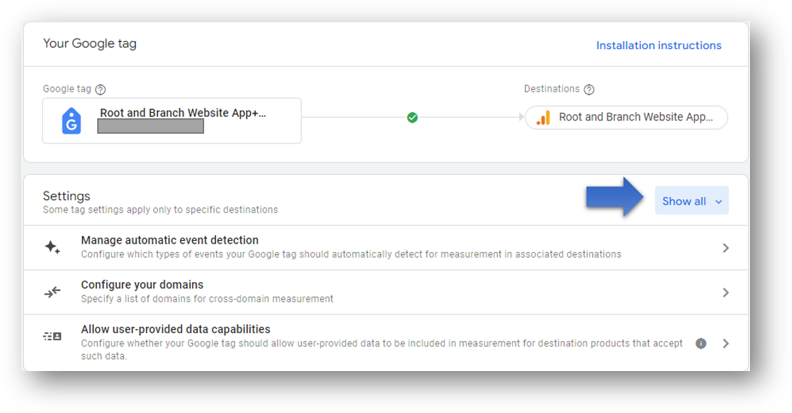
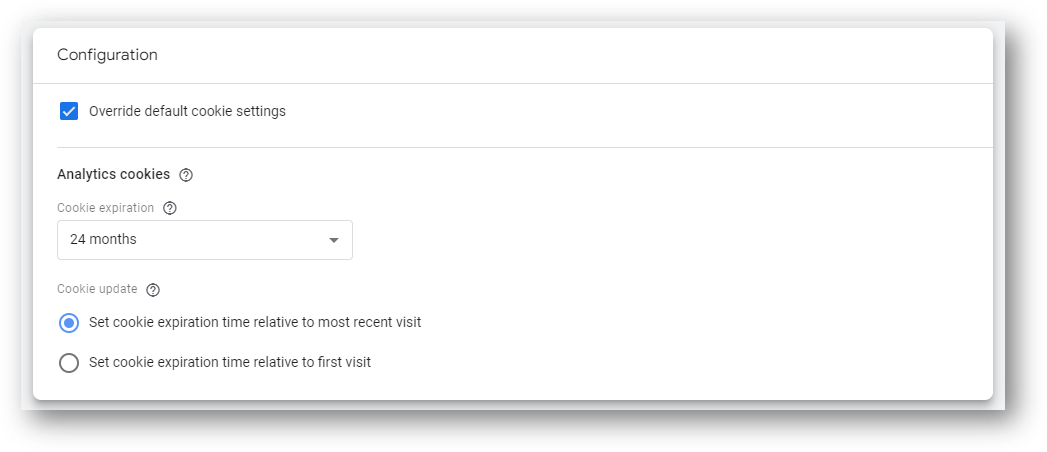
Now, hit the checkbox to ‘Override default cookie settings’. You’ll see options as shown below. This is where you can adjust your ‘Cookie expiration’.
You can also adjust your ‘Cookie update’ if desired. The default is for cookies to expire relative to the most recent visit. However, you can have cookies expire relative to the timing of the first visit, regardless of any subsequent visits.
Reminder: Adjusting your Cookie update would have implications for your GA4 user counts.
Hit the drop down arrow and you can choose your cookie duration. As you can see below, you have the option to have cookies expire immediately when the browser session ends.
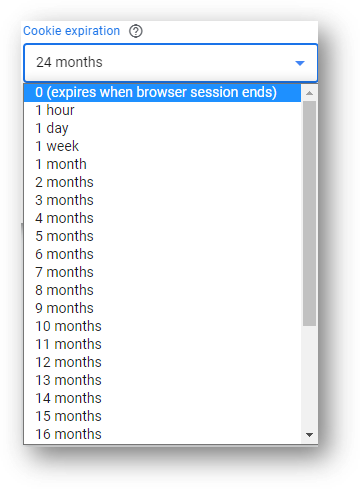
If you don’t want to expire your cookies immediately, you can customize your cookie expiration window differently.
Hit the blue ‘Save’ button in the top right. All done.
What’s Up With Third Party Cookies?
A single domain creates and controls first-party cookies. Third-party cookies track behavior across multiple domains
Advertising networks, retargeting campaigns, and other marketing platforms that span multiple websites use third party cookies. GA4 does not rely on third-party cookies as its primary tracking mechanism.
Advantages and Challenges With Third Party Cookies
Third-party cookies can present both advantages and challenges:
- Enhanced Tracking: Third-party cookies can track users across different websites, allowing advertisers to deliver targeted ads based on their browsing history and interests. This cross-website tracking enables marketers to reach users who have previously engaged with their brand or expressed specific preferences.
- Limitations and Privacy Concerns: Over the past few years, there has been a growing emphasis on user privacy and data protection. Major web browsers have implemented stricter policies regarding third-party cookies, making it more challenging to track users across websites. Privacy concerns and user opt-outs have resulted in limitations for marketers relying solely on third-party cookies.
GA4 Intends to Become Less Reliant on Cookies
Google Analytics has transitioned towards a more privacy-centric approach in GA4. In fact, if you read Google’s initial blog announcement about GA4 the word “privacy” appears no less than 7 times!
While first-party cookies remain a fundamental part of the tracking mechanism, GA4 introduces other data collection methods, such as events and user properties, to reduce reliance on third party cookies.
When Will Google Phase Out Cookies?
Google had said that its plan was to phase out out tracking cookies (third party cookies) in Chrome beginning in early 2024. However, the company reversed course on July 22, 2024. Here is a list of important cookie-related privacy milestones.
- On April 14, 2016 GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) was passed in the EU. This accelerated the demise of the third party cookie.
- Starting on April 26, 2021 Apple introduced a new feature (called App Tracking Transparency) in iOS 14.5 that requires asking users for consent of app tracking.
- March 6, 2024 Google, as part of compliance with the Digital Markets Act (DMA) requires consent mode v2 compliance, particularly in the EEA.
- July 22, 2024 Google reversed course on its plan to get rid of third party cookies. Google says that users will now have control of their own data.
Final Notes About Google Analytics Cookies
Cookies can be confusing. Here are some clarifying notes that may help this all make more sense.
First Party Cookies vs. Events in GA4
First-party cookies primarily maintain session information and track basic visitor information, rather than tracking granular user interactions. Events track those detailed user interactions.
Cookies help to bring all that data together and associates it with a GA4 session. They associate all pageviews, clicks, scrolls, and other events with one another. Without cookies, GA4 can still collect and model data using “cookieless pings” in the Advanced mode of consent mode v2. The specifics though, seem hazy here.
What’s Next?
Interested in digital analytics and need a break from cookies? If you have some time to learn something new, I’d recommend these 3 options to building a quick GA4 events report or this comparison of GA4 vs. Microsoft Clarity.
About Root & Branch
You can learn more about Root & Branch here.









Trackbacks & Pingbacks
[…] If you’re continuing to use Google Analytics, it’s worth understanding things like how cookies work in GA4 and consent […]
[…] more about Google Signals than you did before. For more, you might be interested in reading about cookies in GA4 or consent […]
[…] mode deals with cookies for GA4 and advertising cookies for Google […]
[…] Mode v2 in November of 2023. Consent mode v2 provides functionality for both analytics cookies (GA4 cookies) and advertising cookies (Google Ads […]
[…] event is logged on iOS apps. These events fire if Google Analytics 4 does not see a pre-existing Google Analytics cookie in the browser, so it recognizes that this is new visitor. You can read more from the Google […]
Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!